Table Of Content
It is made of a protein called keratin, compacted and fused together. It has three distinct layers, and is made up of amino acids (proteins) held together by chemical bonds. Hair shaft pigmentation ensures multiple benefits including UV protection, thermoregulation and sexual perceptions.
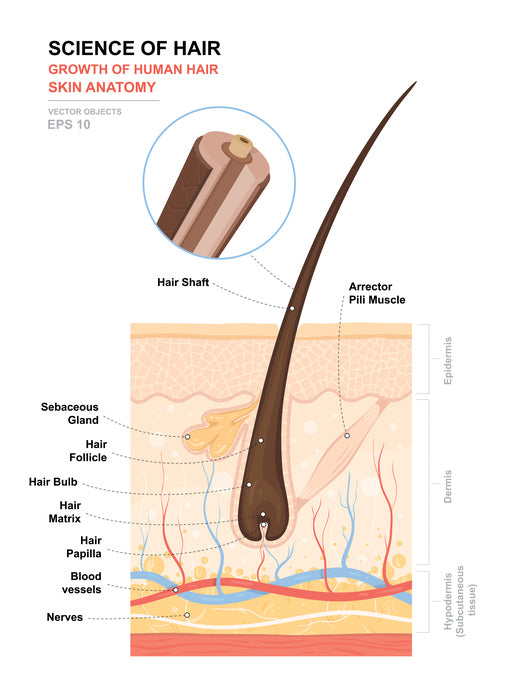
Hair shaft
The genes that are expressed before the signs of hair follicle formation constitute the precise spacing and distribution of the follicles. Iron supports hair growth because it helps to form red blood cells that deliver oxygen and nutrients to the hair follicles. New hair cells then start to multiply at the base of the “empty” hair follicle to form a new hair, and the growth phase of the hair growth cycle starts all over again.
Anatomy, Hair
There are three scales in different types of healthy hair of animals – coronal, spinous, and imbricate. The healthy hair of animals also shows the continuous, discontinuous, fragmented, and stacked medulla. Let’s see some of the hair under microscope labeled diagrams that might help you understand every single feature. Here, I will show you the different labeled diagrams of the hair shaft and follicles.
Anatomy at a Glance
Each follicle has a sebaceous gland that produces lipid-rich sebum (an oil) which naturally protects the hair and moisturizes the scalp. The rate of hair loss may increase noticeably if the hair roots are damaged during the growth phase or if a lot of hairs go into the resting phase at the same time. If no new hair grows and replaces the hair, that part of the skin becomes bald. This type of hair loss is referred to as alopecia – regardless of how large the bald spot is or whether it affects the scalp or body hair. But baldness can also be permanent – one typical example is gradual hair loss in men (male pattern hair loss). It is so difficult to identify the inner and outer root layer of the follicle practically under a light microscope.
Each of your hairs grows from its own individual hair follicle. The hair bulb is situated at the base of each hair follicle, and contains your growing hair cells. These continually divide and push upwards, gradually hardening.
A healthy adult may lose about 70 to 100 hairs on their head per day. But because new hairs are always growing and replacing them, this natural hair loss isn't noticeable. Whether it is straight or curly will depend on the cross-sectional shape of hair. The more oval-shaped the cross-section is, the curlier the hair will be. At the base of the hair, the hair root widens to a round hair bulb.
Your hair shaft consists of three layers

Since hair growth is basically just a collection of dead cells being pushed along apouch (follicle) in the skin, it’s important to learn aboutskin structure and function too. The arrector pili muscle, a tiny bundle of muscle fiber, is attached to the outer sheath. When the muscle contracts, it causes the hair to stand up, otherwise known as goosebumps. The follicle is lined by an inner and outer sheath that protects and molds the growing hair. The inner sheath follows the hair and ends just before the opening of the oil gland, or sebaceous gland. Hairs from different animals show specific characteristic features under the light microscope.
6 Bleached Blond Hair Do's and Don'ts For Men - How to Go Platinum - Men's Health
6 Bleached Blond Hair Do's and Don'ts For Men - How to Go Platinum.
Posted: Wed, 25 May 2022 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Hair typically grows at the rate of 0.3 mm per day during the anagen phase. Hair loss occurs if there is more hair shed than what is replaced and can happen due to hormonal or dietary changes. Hair loss can also result from the aging process, or the influence of hormones. Note the both the internal and the external sheaths are continuous at their base with the papilla. This explains why the quality and appearance of the hair is dependent on the health and well-being of the dermal papilla. The external root sheath of a hair follicle is continuous along with the epidermis.
How to visualize the scales and medulla of hair?
The rest of the hair is anchored in the follicle and it lies below the surface of the skin. The hair root is enveloped by the hair follicle which is a skin appendage that lies deep in the dermis of the skin. The cortex forms the main bulk and pigment (colour) of your hair.
These nerves sense hair movement and are sensitive to even the slightest draft. Again, the cortex of the healthy hair consists of keratin and pigment granules. There are also air sacs (cortical fusi) in the cortex of healthy hair. The fur animal shows very fine to medium diameter, whereas the domestic animals show medium diameter in their hair shaft. Again, the medulla of the fur animal is generally serial or vacuolated, whereas the domestic animal shows the amorphous medulla.
The hair papilla, which supplies the hair root with blood, is found inside the bottom of the hair bulb. New hair cells are constantly being made in the hair bulb, close to the papilla. Each hair follicle is attached to a tiny muscle (arrector pili) that can make the hair stand up.
The color, size, and distribution of the pigment granules may vary within a single hair and among the different species of animals. Again, the oval structures are the solid bodies that are spherical to the oval. The medulla of a human hair may be continuous, fragmented, or absent. They possess a very regular and well-developed medulla in their hair.
You will find a very fine diameter in these crown-like scales compared to the others. There are strong bonds between the amino acids of these helices; thus, these bonds make strong hair. In fact, they are one of the strongest naturally occurring bonds in the world. When you perm it or relax your hair, these disulphide bonds are broken, and reset into a different configuration. This is what allows you to permanently change the shape of your hair. The texture of hair is related to differences in cross-sectional shape—straight hair is round, wavy hair is oval, and tightly curled hair is relatively flat.
It consists of long keratin filaments, which are held together by disulphide and hydrogen bonds. The health of your cortex depends largely on the integrity of the cuticle protecting it. Your hair shaft is the part of your hair that can be seen above your scalp.
No comments:
Post a Comment